Why the Role of Supplementation is Vital in a Woman’s Healthy Diet
Women today are more conscious of their health than ever before, but unfortunately, many still don't get enough vitamins and minerals in their diets. The consequences of this lack can be serious, making supplementation important for women to maintain optimal health. In this article, we'll explore why it's so important that women make sure they're getting the nutrients they need from their diet or a supplement.

The female body needs key vitamins and minerals to stay healthy and function at its best. Women especially require certain essential nutrients & vitamins— like iron, calcium, vitamin D, folate and omega-3 fatty acids, including fat-soluble (A, D, E and K) and water-soluble (B complex and C). — which are often lacking in modern diets due to busy lifestyles and processed foods. Inadequate consumption of any specific vitamin has been linked with negative consequences including weakened immunity, decreased cognitive capacity, and impaired physical performance. To prevent these potential adverse effects, it is vital that women understand their individual nutritional needs and strive to meet them through healthy eating habits combined with targeted supplementation when appropriate. Supplementation can therefore play an important role in providing additional support for those with increased needs or limited access to nutrient rich foods.
For most women, adding dietary supplements is an easy way to ensure you’re getting all the nutrients your body needs each day — no matter how busy life gets! But with so many different kinds of supplements out there on the market today, it can be difficult to know which ones are right for you. That's what we'll help answer here: which supplements should you take as part of your daily routine?
Nutritional Requirements for Women

Women involved in extreme sports like bodybuilding, mixed martial arts, rock climbing, snowboarding and surfing often have greater nutritional needs than the average person. Studies show that a staggering 75% of female athletes don't get enough daily vitamins to meet their nutritional requirements. This is especially concerning when we consider how essential these micronutrients are for optimal physical performance.
Vitamins help our bodies convert food into energy while aiding cell growth and repair. They also contribute to healthy immune systems, which is crucial during intense training regimens or competitions. For women who participate in extreme sport activities, this means supplementing their diets with additional vitamins can be beneficial for maintaining strong bones, muscles and general health.
With extra vitamins, women athletes can reach peak performance levels and stay active for longer periods of time without becoming fatigued or injured more easily. By getting the right amount of nutrients each day, they'll be able to enjoy the rewards of an active lifestyle safely and effectively.

Different Types of Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals come in many forms and vary by type, source, absorption rate, bioavailability, cost, suggested serving size, etc. It is important to understand the different types of vitamins and minerals so that you can make an informed decision about which ones are best for you.
Vitamins have a crucial role in metabolic processes such as energy production from food sources and aiding cell growth. There are two primary categories of vitamins: fat-soluble (A, D E & K) and water soluble (B & C). An example of a fat-soluble vitamin would be Vitamin A which helps maintain healthy vision while Vitamin C—a water-soluble vitamin—promotes wound healing among other benefits.
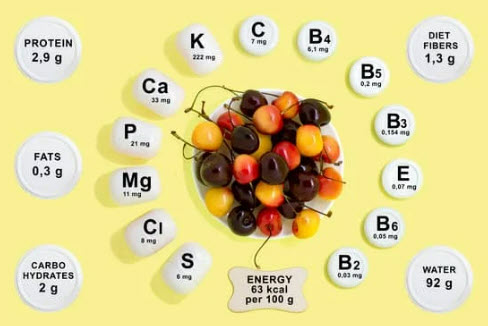
Minerals also play an essential role in human nutrition since they help with everything from metabolism regulation to nerve signals transmission. The most common trace elements include calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc copper, selenium phosphorus and folic acid. For instance, Calcium is needed for strong bones whereas Folic Acid plays an important role in helping red blood cells carry oxygen throughout your body.
Given these facts about vitamins and minerals it’s clear why understanding their differences is critical when considering supplementation options to optimize nutrient intake levels. Women should consult with their physicians before beginning any supplement regimen or making changes to existing habits related to diet or exercise. Furthermore three key nutrients that are often lacking in diets are: Vitamin C; Folic Acid; Vitamin D - all vital components of maintaining overall health.
Assessing Your Vitamin Needs

In order to determine if women are not getting enough vitamins, it is important to assess their individual vitamin needs. A nutritionist can evaluate the diet of a woman and suggest changes that may be beneficial to enhance health or in helping her achieve optimal nutrient intake. Nutrients such as calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc are especially important for female health.
There are several ways to increase nutrient intake including adding fresh fruits and vegetables into meals throughout the day; incorporating lean proteins into your meal plan; eating whole grains like quinoa; consuming low-fat dairy products; limiting processed foods; snacking on nuts and seeds; taking supplements when necessary; drinking plenty of water; exercising regularly; and reducing stress levels whenever possible. Supplementation is key in ensuring that women get all the essential vitamins needed for optimum health.
Reasons Why Women Are Deficient in Vitamins and Minerals
Women are more vulnerable than men to vitamin and mineral deficiencies due to the unique nutritional demands of their bodies. To ensure that they get enough vitamins and minerals and remain healthy, it is important for women to understand why these deficiencies occur in the first place.
Firstly, a strict diet can be a major cause of vitamin deficiency in women. Limiting the food options may be ideal for physical appearance: i.e., building muscle or making weight. However, health is deeper than the outward appearance. All the unseen systems in your body work as a collective to keep you functioning: circulatory, respiratory, nervous, endocrine, immune- these also require supplementation for optimal performance. Secondly, certain medical conditions such as gastrointestinal issues or kidney disease can impair nutrient absorption leading to deficiencies in some vitamins or minerals like vitamin B12 which primarily comes from animal sources. Thirdly, hormonal changes associated with age or pregnancy also contribute to higher needs for certain nutrients. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as stress, over- training, lack of rest prohibit the body's ability to absorb vitamins properly causing further depletion over time. In order for women to stay healthy and maintain optimal well-being throughout life stages it is critical that they receive sufficient amounts of vital nutrients. With informed decisions concerning what we eat and how we live our lives combined with timely supplementation where appropriate; women will find themselves empowered on their path towards achieving good health.
Hormonal Changes That Trigger Vitamin Deficiency

Women may be at an increased risk of vitamin deficiency due to hormonal changes throughout their life. These hormones can affect the absorption and utilization of vitamins in the body, leading to deficiencies. This is especially true during pregnancy when women need more nutrition than ever before.
As a woman's menstrual cycle progresses, hormone levels fluctuate which can lead to nutrient depletion that causes low energy levels and other symptoms such as headaches or nausea. During menopause, estrogen production decreases resulting in decreased iron absorption and an increase in vitamin B12 requirements for proper functioning of red blood cells. Low levels of these essential nutrients can cause fatigue, weak bones, hair loss and even depression.
Because of these possible deficits, it is important for women to get enough vitamins from food sources or take supplements if necessary
Identifying Vitamin Deficiencies
What do vitamin deficiencies look like? How can women determine if they are not getting enough nutrients from their diet, and should consider taking supplements? Identifying vitamin deficiencies is an important step in ensuring optimal health.
The first sign of a vitamin deficiency may be fatigue or general malaise even after adequate rest. Nutritional deficiencies can also cause changes in the skin such as dryness, rashes, discoloration, or acne. Women may have weak immune systems resulting in frequent colds and infections or slow wound healing. Other signs include brittle hair and nails that break easily, muscle weakness, joint pain, headaches, mood swings and depression.
For women who suspect they may have nutritional deficiencies there are tests to confirm the diagnosis including measuring levels of vitamins A, B12 and D3 through blood work. Taking multivitamin supplements containing iron will help reduce symptoms associated with iron-deficiency anemia which can lead to further complications if left untreated. Eating foods rich in vitamins C and E helps boost immunity while supplementing calcium protects bones against osteoporosis later on in life. It is important for women to get tested for nutrient deficiency so that any potential problems can be addressed before it leads to more serious issues down the road.
Nutritionists recommend creating a well-balanced diet by eating plenty of fruits and vegetables every day combined with lean proteins such as fish or poultry along with whole grains like quinoa or oats instead of processed carbohydrates like white bread or potato chips to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients without having to take dietary supplements. However certain medical conditions may require additional supplementation tailored specifically for individual needs so consulting a healthcare provider about nutrition requirements would be beneficial when necessary.
Dietary Sources of Vitamins and Minerals

Achieving and maintaining good health is an intricate process that requires the consumption of essential vitamins and minerals. Naturally occurring sources of these vital nutrients are available in a variety of food items, but many times supplementation may be necessary to fulfill one's daily nutritional needs.
The first step toward understanding how to obtain adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals is to become familiar with their dietary sources.
In addition to being aware of what types of foods contain specific vitamins or minerals it is also important to understand how much should be consumed on a daily basis for optimal health outcomes. The individual requirements vary based on gender, age and physical activity level among other factors so consulting with a nutritionist or healthcare practitioner is recommended when determining the proper amounts needed for healthy living.
Foods To Avoid When Taking Supplements

While supplements can be a great way to get these important micronutrients into your body, there are some foods that should be avoided or limited while taking them. One food in particular that should be avoided when taking supplements is processed meats and fish. These items contain large amounts of sodium and nitrates which can have adverse effects on the absorption rate of certain vitamins. Additionally, they also tend to contain very low levels of other important vitamins and minerals so avoiding them altogether may be beneficial if you’re looking to ensure you’re receiving adequate nutrition from your diet.
Another type of food that should be limited when taking dietary supplements is sugar-sweetened beverages such as sodas, energy drinks, and sweet tea. These products contain high concentrations of added sugars which can interfere with the absorption rate of certain essential nutrients like calcium and magnesium. Therefore, it’s best to limit consumption of sugary drinks while supplementing with multivitamins or specific mineral sources in order to achieve optimal nutrient intake without any interference from these types of beverages.
Overall, understanding what foods to avoid or limit while taking dietary supplements will ensure maximum benefit from them and promote more efficient uptake of vital micronutrients needed for proper functioning throughout the day. Knowing this information can go a long way towards helping people feel their best and maintain an overall sense of wellbeing through conscious lifestyle choices related to nutrition and general health practices.
Synthetic Supplements
When choosing which type of supplement is most suitable for you, synthetic supplements should definitely be taken into consideration. These supplements typically come in pill form and offer several advantages over natural alternatives such as convenience and cost-effectiveness. Synthetic supplements tend to be more reliable than other forms since they contain precise dosages that can easily fit into your lifestyle without any hassle or messiness associated with other types of supplements. Furthermore, due to its precise dosage levels, synthetic supplements are less likely to result in side effects compared to natural alternatives, which often lack accurate measurements and dosing instructions.
Although synthetic supplements may appear attractive at first glance, it is important for women to understand how their bodies respond before taking them regularly. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional prior to use will ensure that any potential risks are minimized while still achieving desired results from the supplementation program chosen. Ultimately, this knowledge provides male and female consumers alike with the freedom necessary to make informed decisions about their overall health and nutrition needs based on individual circumstances.
Risks Of Over-Supplementation
A vivid picture of the risk associated with over-supplementation emerges when one considers the potential consequences. Too much supplementation can lead to an imbalance in essential vitamins and minerals, which may result in a higher risk factor for various diseases. Excess intake of certain vitamins and minerals can have a detrimental effect on cardiovascular health and reproductive age. On top of this, further complications arise due to interactions between different supplements that might increase or decrease their bioavailability and absorption rate.
It is important to be aware of these risks before taking any type of supplement as it could cause more harm than good if taken without proper guidance from healthcare professionals. For instance, individuals should take care not to exceed the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for specific nutrients as this could contribute to adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, constipation and even kidney stones in some cases. Additionally, excessive amounts of fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin A & D can build up in the body tissues leading to hypervitaminosis - a condition where there are high levels of toxic metabolites circulating throughout the body's systems.
Therefore, although dietary supplements provide beneficial nutrition support, they should only be used after consulting doctors or dieticians who can recommend appropriate doses according to individual needs and medical conditions. With adequate knowledge about safety regulations consumers will be able to make informed decisions concerning their health while avoiding potential dangers associated with over-supplementation.
Best Practices for Supplementation
First, determining which type of supplements would benefit an individual woman should involve consulting with a physician or registered nutritionist who can assess her health status and identify any potential nutrient deficiencies. Common supplements include multivitamin-mineral formulas, vitamin D3, omega-3 fatty acids and probiotics. Additionally, specific micronutrients such as iron and calcium may need to be taken separately if needed in higher doses than what is available from a multivitamin-mineral formula.
Second, once supplement selection has been determined, dosage amounts must be considered depending on age group and state of overall health. It is recommended that women take their vitamins at the same time each day but taking them with meals or snacks might improve absorption rate since some vitamins require fat to be absorbed properly by the body. Lastly, general safety measures should also be kept in mind such as avoiding excessive intakes beyond recommended daily allowance levels through diet and/or supplementation combined; additionally, it’s better to buy high quality brands from trusted manufacturers to avoid potential contamination issues due to poor quality control standards used by some companies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Best Way to Determine My Individual Vitamin and Mineral Needs?
With the increasing trend of busy lifestyles, it is no surprise that many individuals are not getting enough vitamins and minerals in their diets. In fact, a recent survey found that almost 65% of Americans do not meet the recommended daily values for micronutrients such as magnesium, zinc and vitamin D. This highlights the importance of determining one's individual needs when supplementing with vitamins and minerals.
When considering what supplements to take, the best approach is to first gain an understanding of your overall health status by speaking with a healthcare professional or nutritionist who can assess dietary habits and lifestyle factors from a comprehensive point of view. The amount and type of supplementation required will vary depending on existing deficiencies and underlying health conditions, so seeking out professional advice is always advised.
In addition to consulting with a healthcare practitioner there are also some helpful resources available online that provide guidance on how to assess nutritional needs based on age, gender, activity level and other life stages. These include tools such as nutrient calculators which estimate energy requirements according to body weight and size; food intake analysis whereby your diet is tracked over several days; or even more general guides related to certain nutrients like Vitamin A or B12 which suggest foods high in these substances plus appropriate dosages if necessary.
To ensure optimal health benefits it is important to have accurate information about your own personal vitamin and mineral needs. With this knowledge you can then make decisions regarding supplementation accordingly:
- Choose products that contain only clinically-tested ingredients
- Ensure quality assurance through third party certification
- Take into consideration drug interactions before taking any new supplements - Follow dosage instructions carefully and consult your healthcare provider if any adverse reactions occur.
What Are the Differences Between Natural and Synthetic Supplements?
When it comes to determining individual vitamin and mineral needs, understanding the differences between natural and synthetic supplements is of utmost importance. Natural dietary supplements are derived from food sources that provide a variety of nutrients including vitamins, minerals, enzymes and antioxidants. Synthetic supplements contain isolated compounds created in laboratories using chemical processes. Both types can be beneficial when used correctly; however, there are some notable distinctions between them.
With natural supplements, consumers have access to a wide range of options as they can be obtained through various food sources such as fruits, vegetables, grains and herbs. They also tend to include multiple essential components which work together synergistically for enhanced effectiveness. Moreover, these products often boast additional health benefits compared to their synthetic counterparts due to their higher concentrations of bioactive substances like polyphenols or flavonoids.
Synthetic supplements consist mainly of concentrated forms of single-constituent ingredients with limited amounts of active components present in the final product. In addition, many laboratory-made additives may be added during manufacturing process to enhance flavor or texture but ultimately leave less room for naturally occurring beneficial substances found in foods like whole grains or nuts. Furthermore, production costs associated with synthesizing compounds can lead to increased prices when compared to unprocessed items typically consumed by humans throughout history.
In conclusion, both natural and synthetic dietary supplements offer potential advantages depending on an individual’s specific nutritional needs and lifestyle habits; thus, providing a range of choices for those seeking supplementation beyond what is offered in traditional diets alone. Ultimately though, it is best practice to consult a nutritionist about supplementing one's diet since each person requires different levels of nutrients based on their age and other factors unique to themselves.
What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Vitamin And Mineral Deficiencies?
When it comes to vitamins and minerals, deficiencies can have serious consequences on overall health. Knowing the most common symptoms of vitamin and mineral deficiencies is crucial for anyone looking to maintain their wellbeing:
1. Fatigue: Vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that cannot be relieved by rest.
2. Anemia: Iron deficiency is one of the leading causes of anemia, a condition in which red blood cells are unable to deliver enough oxygen to the blood cells healthy body's tissues.
3. Brittle nails: A lack of biotin, also known as vitamin H, may lead to brittle fingernails that break easily and appear ridged or grooved.
The effects of vitamin and mineral deficiencies extend beyond just these three symptoms. Other signs include decreased immune function, hair loss, joint pain and confusion—all issues that can cause significant disruptions in day-to-day life if left untreated. Nutritionists suggest regularly consuming foods rich in essential nutrients such as leafy green vegetables, nuts, legumes and whole grains; however, supplementation may still be necessary depending on individual diet needs or preferences.
In addition to dietary sources of vitamins and minerals, there are two main types of supplements available: natural supplements derived from plant extracts and synthetic supplements made from chemically isolated compounds found naturally within plants. Natural supplements tend to work more slowly than synthetic ones due to the presence of other elements present alongside active ingredients; but conversely, they provide stronger long-term benefits since those other elements help enhance absorption rates in the body over time. When choosing between natural or synthetic forms of supplementation, it’s important for individuals to consider what best fits their lifestyle while also having access to reliable scientific evidence regarding effectiveness and safety profiles before making any decisions regarding supplement use.
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies can manifest in numerous ways that vary across different people; understanding potential signs early helps ensure proper nutrition is maintained throughout life no matter what circumstances arise along the journey towards freedom through good health habits!
Are There Any Foods I Should Avoid When Taking Supplements?
When considering the use of dietary supplements, it is important to understand what foods should and should not be consumed while taking them. By understanding potential interactions with certain food items and how they can affect the body’s absorption rate, individuals can make sure they are getting the most out of their vitamins and minerals.
The first step in determining which foods may interact negatively with supplements is to consult a medical professional or nutritionist as each individual has different needs depending on age, gender, lifestyle, etc. Generally speaking, there are some common categories of food that have been linked to interfering with supplement absorption such as dairy products, antacids containing aluminum hydroxide or calcium carbonate, caffeine-containing beverages such as coffee or tea, alcohol consumption, iron-rich foods like spinach or broccoli and high fiber diets. It is best to avoid these types of foods when consuming any type of dietary supplement for optimal results.
For those looking for specific recommendations on what to consume alongside their vitamins or minerals, selecting natural sources rather than processed ones is always a good starting point. Natural sources include fresh fruits and vegetables that provide essential nutrients needed by the body for overall health and wellness. Additionally, increasing daily water intake helps to flush out toxins from the body while also helping with digestion – both key components in making sure your supplements are absorbed efficiently by your system.
By carefully monitoring one's diet while incorporating dietary supplements into their routine regimen and consulting a medical professional, if necessary, before doing so, individuals can ensure they are receiving maximum benefit from their supplementation efforts without compromising other aspects of their wellbeing.
What Are the Potential Risks of Taking Too Many Supplements?
Taking too many supplements can be a risky endeavor, and it is important to understand the potential risks before embarking on such an action. Nutritionists are often consulted for advice when discussing dietary supplementation, as knowledge of vitamins and minerals necessary for optimal health is essential in avoiding any potential drawbacks associated with over-supplementation. Coincidentally, understanding both the benefits and dangers of taking too many supplements can help people achieve greater freedom in their lives.
The first danger that comes with consuming excessive amounts of supplementations is that certain nutrients may become toxic if taken at levels beyond what is recommended by experts. For instance, vitamin A toxicity can occur from intake above 10 times the recommended daily amount. Increasing consumption past this limit has been linked to liver damage, decreased bone density, hair loss, nausea, headaches and blurred vision among other side effects. Additionally, high doses of some fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin D pose serious risk due to their ability to accumulate in body tissues over time.
Excessive supplemental nutrient intake can also interfere with the absorption of other essential minerals and vitamins needed for good health; calcium inhibits iron absorption while zinc blocks copper absorption should they be consumed together or within close proximity to one another. Moreover, several studies have found significant associations between higher intakes of antioxidants such as beta carotene, Vitamin E and selenium with increased mortality rates from various causes including cancer and coronary heart disease; these findings suggest that there could be a threshold effect regarding antioxidant supplement use where more does not necessarily equate to better results.
Given the complex nature of nutrition science today it is prudent to discuss supplement usage plans with a qualified healthcare professional prior to starting any regimen. This is especially true given recent research indicating that even moderate levels of supplementation - lower than those considered dangerous - could still lead to adverse outcomes depending on individual circumstances. Therefore, knowing how much someone needs versus how much they are actually taking will help ensure safe practices when navigating the world of dietary supplementation.
Conclusion
It is clear that women are not getting enough vitamins and minerals in their diets, making supplementation a necessary part of maintaining overall health. Supplementation can help fill the gaps left by an inadequate diet while still ensuring proper nutrition. The key to success, however, lies in understanding one's individual needs and being aware of potential risks associated with taking too many supplements.
By researching different options for natural and synthetic supplements, as well as avoiding potentially harmful foods when taking them, individuals may be able to better determine what works best for them personally. Furthermore, recognizing the symptoms of vitamin and mineral deficiencies can alert someone who might need more support from these types of products.
Ultimately, it is essential for women to ensure they are receiving the nutrients their bodies require through a balanced diet supplemented with appropriate levels of vitamins and minerals. By following this approach, not only will women be able to maintain strong physical health but also enjoy an increased sense of wellbeing due to having properly nourished bodies.
